Peptides in cosmetics

Peptides, the skin’s natural messengers
Peptides are used everywhere in cosmetics. From skin care and hair care to body care and sun care.
Around 7 600 new products, dedicated to cosmetics containing peptide-based ingredients, are launched every year around the world*. One of the main reasons for this is that peptides work.
But not all peptide's molecules have the same function. It is important to understand that only very specific endogenous peptide's sequences are involved in cell metabolism as upstream regulating messengers.
It works like a key and a keyhole. Specific peptide sequences trigger specific protein production, and when it comes to skin proteins like collagen or elastin, the beauty possibilities are clear.
As the forerunner in peptide development for cosmetic applications, Croda Beauty Actives has developed a full range of peptide's sequences to answer various beauty concerns.
The guaranteed efficacy of our peptides is proven through rigorous scientific testing.
*Source Mintel GNPD
Wondering how peptides work?
Watch the video to learn more about how we created our peptides.
37 years of expertise
Peptides or how to combine efficacy and sustainability
Peptide's ingredients are already safe, stable and easy to formulate so any attempts to reduce their impact on the environment is focused on their manufacturing mode.
Less solvents, infinite possibilities:
At Croda Beauty Actives the reduction of solvents reaches 86% for the last 6 years with no more CMRs. Our peptides are TFA-free or will be soon.
Responsibly Sourced Palm Derivatives (RSPO Certified)
Some peptide's peptides include a palmitic chain to enable their bioavailability. At Croda Beauty, the palm derivatives used in low amounts to produce these peptides are RSPO certified according to Mass Balance (MB) supply chain model.Group Assisted Purification Peptide Synthesis (GAP-PS)
A smarter, better way to make bioactive peptide: Our innovative proprietary GAPPS technology combines the best of well-known solid and liquid-phase peptide synthesis, enabling faster and cleaner peptide production. This hybrid approach reduces the use of solvents by replacing many with water, improves yields, and minimises hazardous waste, addressing the traditional challenges of peptide manufacturing. By making complex peptide synthesis more flexible, sustainable, and efficient, GAPPS offers a new responsible, high-performance route to peptide production.
Synthetic peptides are traditionally made using either solid-phase (SPPS) or liquid-phase (LPPS) synthesis. Each technology offers advantages and limitations such as high solvent use, multiple steps, long production time and waste generation.
Our proprietary GAP Peptide Synthesis (GAPPS) overcomes these limitations by uniquely combining the best of both methods. Reactions occur in solution at high concentration, improving yield while reducing solvent use and raw material waste. The process is a more sustainable and efficient way to produce peptides without compromising performance and reflects Croda’s commitment to green chemistry and responsible innovation.
GAPPS vs SPPS: Cleaner, more efficient peptide route.
Using published data from a leading peptide manufacturer, GAPPS was compared with traditional solid-phase synthesis (SPPS) using a 5 amino acid sequence peptide. The results evidenced GAPPS to be more sustainable with:
- Highly efficient amino acid coupling reactions
- 60% solvent use reduction
- Use of sustainably sourced solvent
- Minimised raw material waste
- Higher crude peptide purity (reducing purification steps)
GAPPS uses solvents far more efficiently than traditional SPPS, which requires large volumes for resin suspension, swelling, and washing. GAPPS reactions occur in solution, uses greener solvents and water, making the process more environmentally friendly and sustainable.
Finally, GAPPS increases throughput and process efficiency compared to SPPS and LPPS by supporting higher peptide loading, faster processing, and simplified extraction steps.
Reinventing peptides with synthetic biology
Advanced development programs now allow peptides to be produced without solvents (except water) using synthetic biotechnology to modify micro-organism hosts such as bacteria, yeasts and microalgae. Synthetic biology is a multi-disciplinary field combining microbiology, molecular biology, mathematical modelisation bioinformatics, genetic engineering… to design biological systems that do not exist naturally or to modify existing ones. Finally, this technology allows to develop specific molecules that are then produced using precision fermentation.
This innovative approach offers environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional peptide production, which often relies on solvents, catalysts, or other less sustainable materials. It can also enhance manufacturing efficiency, improving yields and reducing production time and resource consumption.
Croda Beauty proudly introduced Kerabio™ K31, the first human hair keratin fragment peptide developed through synthetic biology, a first-ever recombinant hair repair keratin from an ingredient supplier.
Encapsulated peptides: precision and performance for every skin layer
Unlike other cosmetic actives such as retinol or vitamin C, bioactive peptides are well-tolerated, with lower risk of degradation or skin sensitisation. However, this hero ingredients’ performance can be further increased via precision delivery systems technology. This dual technology approach brings benefits from controlled release and targeted delivery to enhanced effectiveness.
Peptides compounds promote benefits to different layers of the skin, and reaching the correct target can be a challenge. Innovative delivery systems, such as lipid capsules, help stabilise peptides and guide them to specific skin layers, improving performance. Today, these delivery systems are naturally derived, biodegradable, and highly stable, offering a sustainable and effective way to maximize the benefits of cosmetic peptides.
Delivering peptides to specific layers of the skin requires understanding both their biological effects and physical properties. Custom-designed delivery systems, such as submicron particles, can help ensure peptides reach the right layer, release gradually, and work effectively.
Traditional delivery systems, like liposomes, can be unstable in emulsions and sensitive to surfactants, limiting their effectiveness. Newer lipid-based systems, with a central oil core surrounded by lipids and waxes, overcome these limitations. They allow peptides to be incorporated into final formulations more reliably.
Depending on the intended target within the skin, peptides can either be:
- Anchored on the surface of the particle (portage) for immediate action in the upper layers, or
- Encapsulated within the core for controlled release to deeper layers.
This approach protects peptides, enhances their activity, and ensures they perform optimally where they are needed.
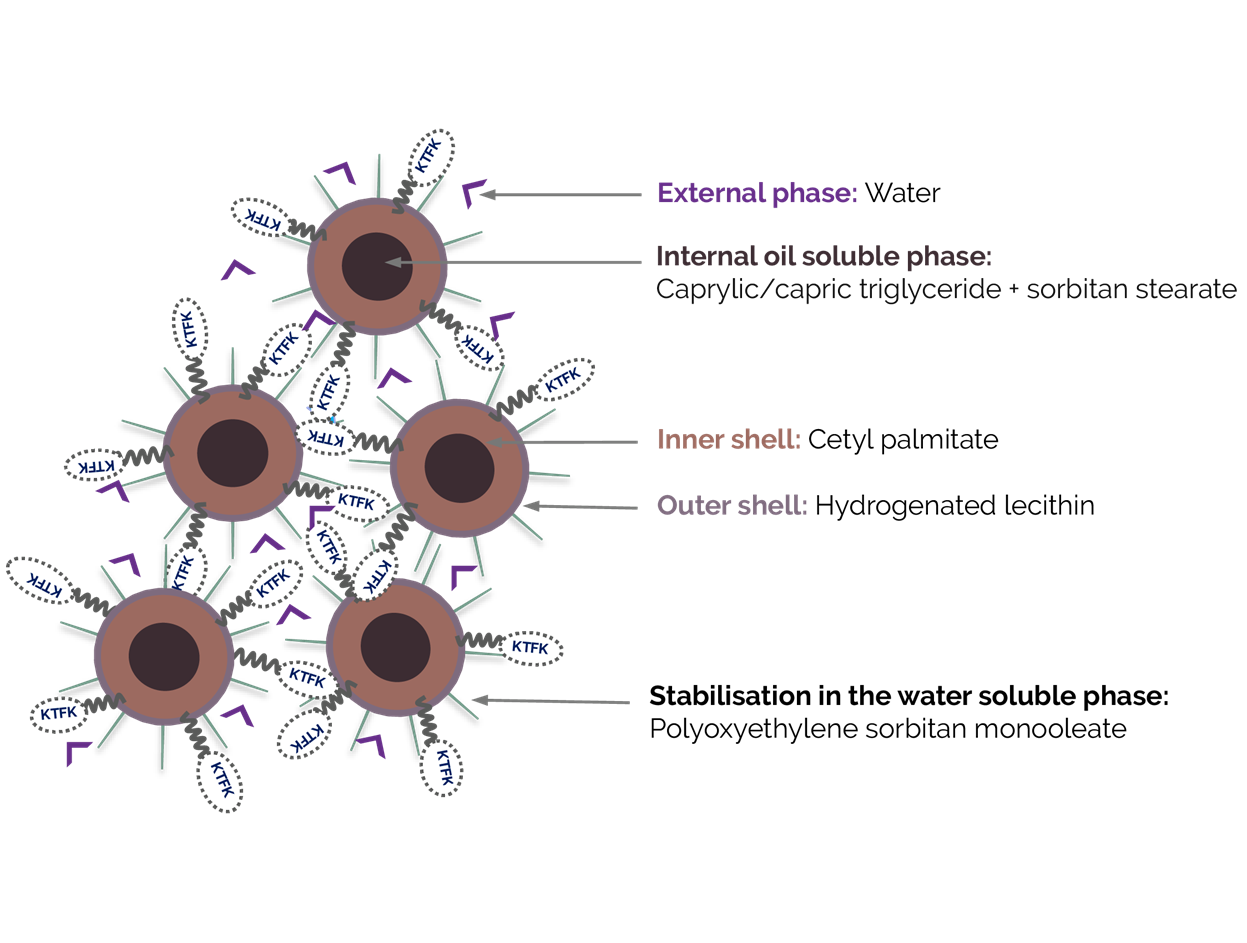
fig 1. example of peptide encapsulation for optimal delivery to the epidermis. Case of Crystalide™
Older delivery systems like liposomes are sensitive to surfactants and are usually unstable in emulsions. The latest generation of lipid delivery systems, consisting of a central oil core surrounded by a mixture of lipids and waxes, circumvents this issue and facilitates the incorporation of peptides in final formulations.
Delivering peptides to the skin’s specific targets can be achieved with deep understanding of the biological effects of the molecule, as well as its physico-chemical characteristics. Unique and specific design of delivery systems, like submicron particles, can allow protection and stabilisation and at the same time control the release, increase the activity, and reduce issues.
*Number of owned publication in third party media
**Number of peptide-based products manufactured Croda Beauty Actives

